⎮ 초기화(intialization)
Swift에서 초기화하는 방법은 다양합니다
let a = "hello, world!" // 타입 추론(type inference)
let b = String("hello, world!") // 타입 추론 + 명시적 초기화
let c: String = .init("hello, world!") // 초기화 함수 사용
let d: String = "hello, world!" // 타입 명시(type annotation)
개발을 완전 처음 배울 때는 명시적으로 타입 어노테이션을 하다가
점점 타입 추론에 빠져듭니다
(Swift는 타입 추론 기능이 강력해요! 뭐 이런 말을 듣기도 하고...)
그러다 개발에 어느정도 익숙해지면 .init을 사용하게 됩니다
예를 들면 TableView cell 같은데서..
그러면, 각각의 초기화 구문은 컴파일 타임에서 어떤 차이가 있을까요?
d는 타입 추론을 하지 않도록 도와주니까 a보다 더 시간이 빠를까요?
⎮ 초기화(intialization)에 걸리는 시간
가장 직관적으로 시간을 확인할 수 있는 방법은 Date()를 사용하는 방법이라고 생각하고 테스트를 했습니다
let time = Date()
for _ in 0..<100000 {
_ = "hello, world"
}
let endTime = Date()
let timeResult = endTime.timeIntervalSince(time)
print("\(timeResult)초")
// 결과 : 0.3355579376220703초
근데 위 코드는 "hello, world"라는 string을 10만번 만들었을 때 얼마나 걸리냐에 대한 테스트
즉, '런타임'의 테스트라서 적절한 테스트가 아닙니다
그러면 컴파일 타임의 비교는 어떻게 할 수 있을까요?
외국 엉님들의 글을 보다가 hyperfine을 사용한 방법을 확인할 수 있었습니다
let a = "hello, world!" // 타입 추론(type inference)
let b = String("hello, world!") // 타입 추론 + 명시적 초기화
let c: String = .init("hello, world!") // 초기화 함수 사용
let d: String = "hello, world!" // 타입 명시(type annotation)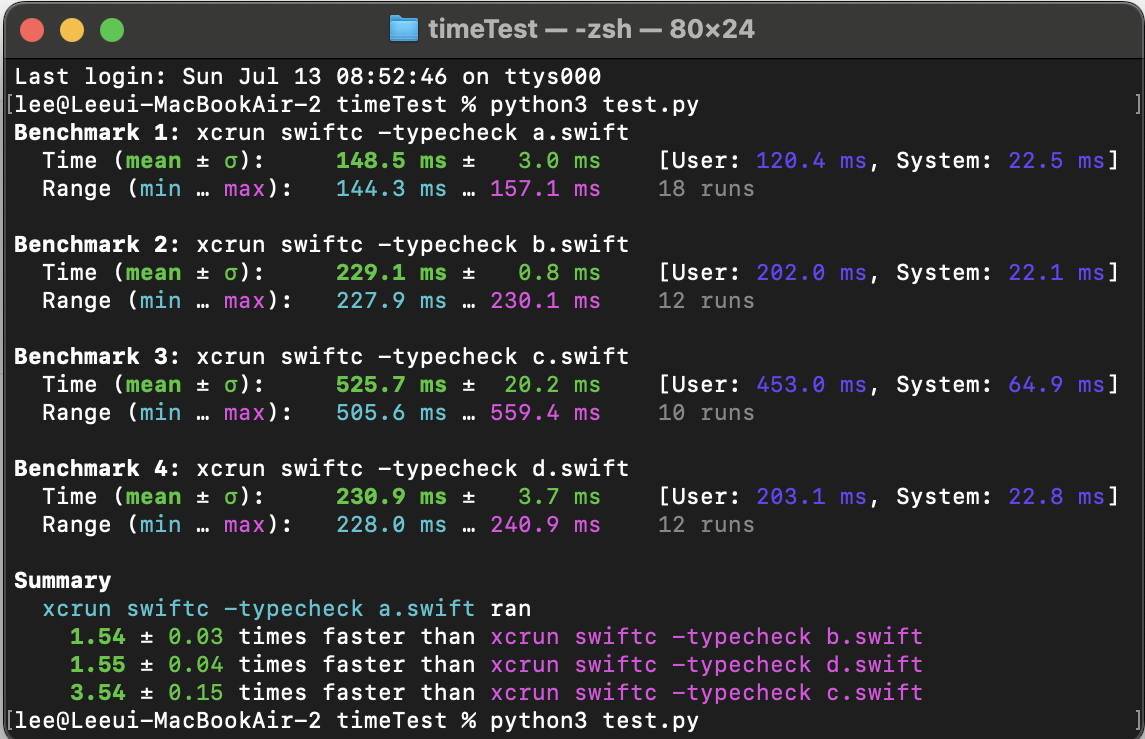
[실행 시간]
a: 144.3ms ~ 157.1ms → 0.144초 ~ 0.157초
b: 227.9ms ~ 230.1ms → 0.228초 ~ 0.230초
c: 505.6ms ~ 559.4ms → 0.506초 ~ 0.559초
d: 228.0ms ~ 240.9ms → 0.228초 ~ 0.241초
a → b -> d -> c 순 (사실상 b와 d는 거의 비슷하고 테스트할 때마다 순서도 항상 바뀐다)
쉽게 생각해보면 d는 타입을 명시해주니까 가장 빠를거 같은데,
사실상 타입 추론인 a가 가장 빠릅니다
⎮ 결론
타입 추론이 가장 빠릅니다
0.n초 차이니까 본인이 선호하는 방식으로 초기화를 해도 무방할 것 같습니다
다만, 어떤 차이가 나는지 정도는 알고 쓰면 좋을거 같습니다!
⎮ hyperfine으로 테스트하는 방법
1. 터미널에서 hyperfine을 설치해줍니다
brew install hyperfine

2. 텍스트 편집기를 열어서 test.py라는 파이썬 파일을 만들어줍니다
import os
filenames = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
code = [
'let a{} = "hello, world"',
'let b{}: String = "hello, world"',
'let c{}: String = .init("hello, world")',
'let d{}: String = "hello, world"'
]
for i, filename in enumerate(filenames):
with open(filename + ".swift", "w") as f:
s = ""
for j in range(1000):
s += (code[i] + '\n').format(j)
f.write(s)
os.system("hyperfine 'xcrun swiftc -typecheck a.swift' 'xcrun swiftc -typecheck b.swift' 'xcrun swiftc -typecheck c.swift' 'xcrun swiftc -typecheck d.swift'")
이렇게 하면 위 파일이 실행될 때, 다음과 같은 1000개의 구문을 만들어줍니다
let a0 = "hello, world"
let a1 = "hello, world"
let a2 = "hello, world"
let a3 = "hello, world"
let a4 = "hello, world"
let a5 = "hello, world"
let a6 = "hello, world"
let a7 = "hello, world"
let a8 = "hello, world"
let a9 = "hello, world"
...
뭐 이런식으로..
구문이 1개면 시간이 너무 짧으니까 1000개정도는 되어야 시간이 누적되면서 시간 측정에 의의가 있습니다
3. 터미널을 열고 python3 test.py를 입력해줍니다

결과를 확인하면 끝~
⎮ Reference
Base: SeSAC 내부 비공개 강의 자료
https://forums.swift.org/t/regarding-swift-type-inference-compile-time-performance/49748
Regarding Swift type inference compile-time performance
Hey all! This came up during a discussion today and I honestly wasn't sure if my assumptions were correct so looking for some clarity here! 🤞 What are the compile-time performance differences between the four declarations below? (I have added how I thin
forums.swift.org
'Swift > TOPIC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Swift | GCD와 Swift Concurrency (0) | 2025.08.26 |
|---|---|
| Swift | translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints는 왜 끄는걸까? (2) | 2025.07.20 |
| Swift | UserDefaults는 어디에 저장될까? (+ PropertyWrapper) (1) | 2025.07.09 |
| Swift | iOS App 최적화 - App Thinning (2) | 2025.07.09 |
| Swift | ABI Stability - ABI 안정성 (2) | 2025.07.07 |

